Ectropion
.jpg)
Ectropion
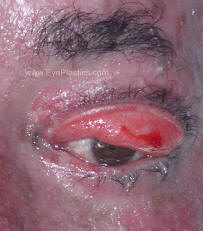
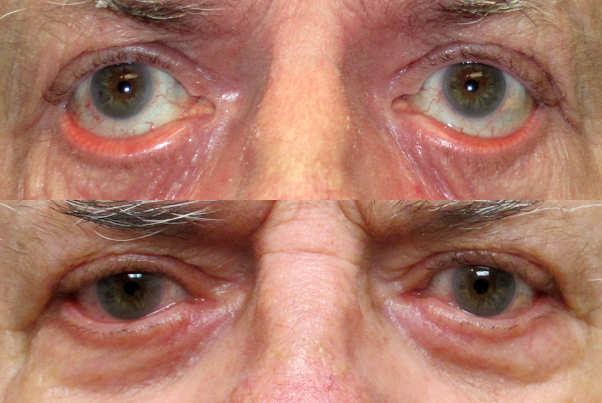
- Ectropion is the medical term used to depict sagging and outward turning of the lower eyelid and eyelashes.
- The margin of the eyelid and the eyelashes evert (turn out) .
- This rubbing can lead to excessive tearing, crusting of the eyelid, mucous discharge and irritation of the eye.
- During blinking, the eyelids normally sweep across the surface of the cornea (Tearing occurs because the eyelids are not able to wipe the surface of the cornea perfectly to pump the tears into the tear duct.
- Most cases of entropion are due to relaxation of the tissues of the eyelid as a lead to of aging. Some cases lead to from scarring of the eyelid caused by chemical and thermal burns, trauma, skin cancers, or previous eyelid surgery. Rarely Ectropion can be present at birth if the eyelids do not form perfectly.
Classification of Ectropion
- Involutional
- Paralytic
- Cicatricial
- Mechanical
-
Involutional Ectropion
Etiology: due to horizontal laxity
- Treatment: lateral canthoplasty, full thickness pentagonal wedge resection
- Involutional
Cicatrical Ectropion
- burns
- trauma
- ocular rosecea
- dermatitis including eczema
- chronic inflammations suchas as erythema multiforme, bullous pemphigoid, sarcoid, icthiosis
- zoster
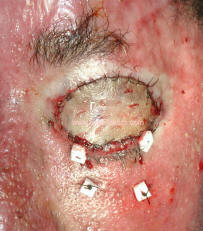
Treatment: lubrication, surgery (skin graft for vertical elongation) Photographs below show a patient who sustained SEVERE facial burns, with resultant cicatrical changes, complete eversion of the left upper eyelid with scarring of the lid margin/lashes to the area of the eyelid crease
To its left, is a photograph immediately after surgery. A skin graft was placed to release the scar and un-fold the upper eyelid.
Paralytic
Anatomy & Function of the facial nerve
- The facial nerve (CNVII) has two major divisions and controls the muscles of facial expression, including the frontalis muscle (raises the eyebrows), the orbicularis oculi muscle (closes the eyes), the zygomaticus muscles (raises the angle of the mouth)
- The upper zygomatic branch supplies the frontalis, upper lid orbicularis oculi, corregator supercilli and procerus.
- The lower zyqomatic branch supplies the lower lid orbicularis.
- The nervus intermedius gives off the greater petrosal nerve which carries parasympathetic secretary fibers to the lacrimal gland
Etiologies
- Congenital
- Acquired
- Bell's Palsy
- vascular lesions
- Tumors Trauma
- Acoustic Neuroma
- Parotid gland
- temporal bone tumor
Symptoms
Treatment:
-
- Medical
- Temporary: Lubrication, moisture chamber
- Surgical
- Permanent: lateral tarsorraphy permis closure of the eyelids to narrow the palpebral fissure and decrease evaporation.
- Brow suspension,
- fascia lata or silicone sling to lower eyelid
- gold weight insertion a light (1 mg weight ) manufactured by Meddev Corp is fixed to pretarsal space of the upper eyelid. This weight allows the eyelid to close more easily.
Punctal Ectropion
Suirgical Treatments
.jpg)